Adiabatic Process An adiabatic process is one in which no heat is gained or lost by the system In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: adiábatos, “impassable”) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment.Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings only as work The mathematical representation of the adiabatic process is

Adiabatic Processes

Derivation of expression for work done in Adiabatic process - YouTube

Adiabatic Process and Applications of Adiabatic Process | IIT JEE and NEET Physics

Work done in an Adiabatic process

Work done in an Adiabatic process - YouTube

Adiabatic Expansion (AQ = 0)

Adiabatic - Energy Education
The mathematical representation of the adiabatic process is adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no heat transfer from in or out of the system For an ideal gas, an adiabatic process is a reversible process with constant entropy

Adiabatic Process - Definition, Equation, Reversible Adiabatic Process, Example, Differences, Video and FAQs
An Adiabatic process undergoes in such a way that no heat enters or leaves the system during the whole process i.e. The first law of thermodynamics with Q=0 shows that all the change in internal energy is in the form of work done adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which there is no heat transfer from in or out of the system

Chapter 2: The First Law of Thermodynamics for Closed Systems – Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics with Q=0 shows that all the change in internal energy is in the form of work done As a key concept in thermodynamics, the For a reversible adiabatic process, the integral amount of work done during the process depends only on the initial and final states of the process, and is the one and the same for every intermediate path.

Chapter 5 Continued More Topics in Classical Thermodynamics
What is adiabatic process? Calculate the work done for adiabatic expansion of a gas. - Quora
Work and Temperature Expressions for Adiabatic Expansion of Ideal Gas Both Adiabatic and Isothermal processes are integral part of thermodynamics but both of them are totally different from each other For an adiabatic process, and thus the integral amount work done is equal to the change in internal energy
Work done in an Isothermal Process
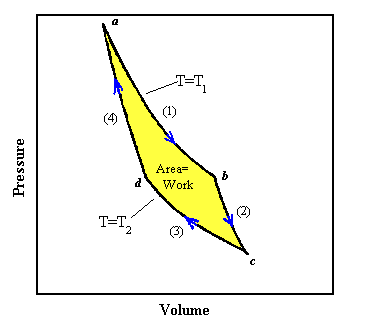
The second law of thermodynamics
An Adiabatic process undergoes in such a way that no heat enters or leaves the system during the whole process i.e. In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: adiábatos, “impassable”) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment.Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings only as work This condition can be used to derive the expression for the work done

Thermodynamics, PV Diagrams, Internal Energy, Heat, Work, Isothermal, Adiabatic, Isobaric, Physics - YouTube

Chapter 6 | Thermodynamics

Adiabatic conditions